
Every company needs to be aware of the implications of investing in fossil fuels, or alternative energy. Companies need to know what they gain and lose in the short and long term.
However, to be able to weigh these options, it is first advisable to take a closer look at both energy sources.
We have already discussed energy sources and the pros and cons of renewable energy. In this article, we will focus on non-renewable energy sources.
-
Which energy carriers are considered non-renewable?
-
What are their characteristics and how do they affect the environment?
Non-renewable vs renewable energy sources
Renewable energy is the energy we obtain from sources that never run out. These include, among others:
-
Solar energy
-
Wind energy
-
Biomass
Although these are the most common alternative energy sources, there are many others. The less commonly used renewable energy sources include:
-
Hydropower
-
Energy from ocean waves
-
Tidal energy
-
Geothermal energy
What are non-renewable energy sources?
Everything that cannot be renewed or regenerated on a human scale – only over millions of years – is considered a non-renewable energy source.
As our article on natural gas explains, these resources are formed from dead animal and plant remains that decompose and eventually move into deeper layers of the soil. Over millions of years, they migrate through the cracks in the rocks to form huge oil and gas deposits.
How do renewable and non-renewable resources differ?
The process itself cannot be artificially replicated under accelerated conditions, so the organic matter that is currently decomposing will only appear as a fossil fuel in the Earth's ecosystem much later.
The two main reasons for the impending disappearance of non-renewable energy sources:
-
The slow regeneration of fossil energy
-
The excessive consumption of humanity
The result:
-
There is barely over 100 years' worth of coal left.
-
There is even less natural gas left, barely enough for 50 years.
-
Humanity is in the worst position with oil, as there is not even enough for 50 years.
Look at a comparison of the use of renewable and non-renewable energy sources in terms of their ratios.
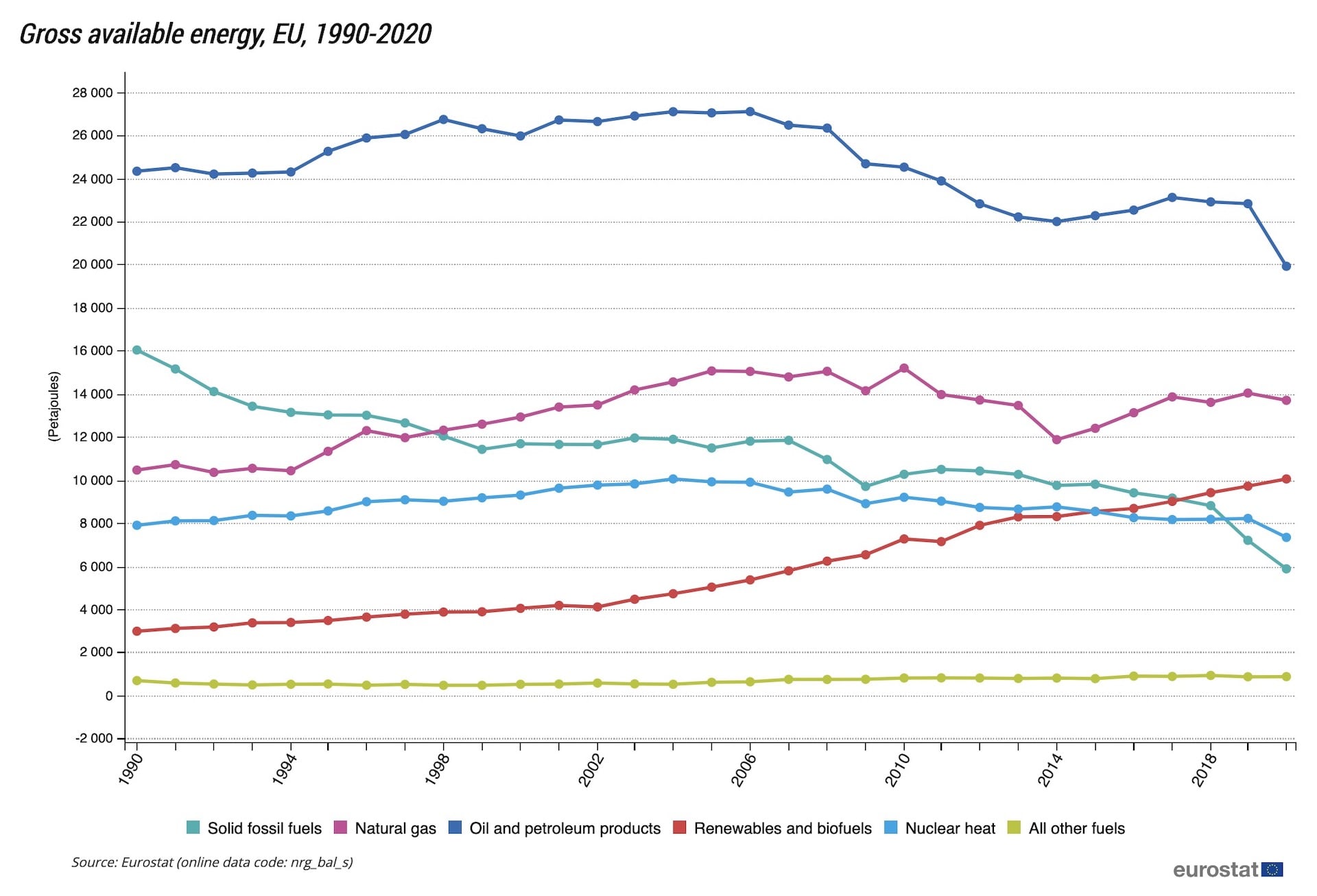
Source: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Energy_statistics_-_an_overview
The question is: if there is so little left of them, why does humanity rely on these energy sources so heavily?
How does non-renewable energy work?
To use the fossil energy sources extracted from the lower layers of the earth, refined and transported, the following processes must take place:
-
The incoming energy sources are burned.
-
This generates a large amount of steam.
-
The destination of the steam is a turbine.
-
The generator is responsible for producing electrical energy from the steam-driven turbine.
Of course, non-renewable energy can be used in many other ways. Just think of the operating principle of internal combustion engines in our everyday vehicles. It is therefore clear that we can solve the use of the same energy source in many different ways.
After extraction comes transportation. Today, millions of kilometers of gas pipelines run through our planet – and where it is not possible to reach through them, tankers are used (e.g. LNG gas).
Humanity has built a well-functioning distribution system with great precision and efficiency over the past few centuries, which cannot be replaced overnight. However, the world is undoubtedly heading towards this – and not just because we are running out of fossil fuels.
The disadvantages of fossil fuels
Coal, oil, and gas are undoubtedly the most "efficient" sources of energy currently in use, but they come at a high cost that researchers have only begun to discover in recent decades.
Today, however, everyone is aware of this, as the use of non-renewable energy sources pollutes the environment to an extraordinary extent, with very serious consequences. It is no wonder that the phenomenon known as "climate anxiety" is becoming increasingly common, which is not yet recognized as a clinical illness, but more and more people are suffering from it.
Undoubtedly, coal is the most polluting fossil material, the most commonly used energy source in the early industrial revolutions. Its use is now declining, which has a favourable effect on the ecosystem of our planet, as natural gas is much less polluting – but even this cannot be considered environmentally friendly.
Conclusion
Perhaps humanity recognized the problem in time, and active steps have been taken toward solving the problem:
-
Nations signed the Kyoto Protocol
-
This was followed shortly after by the Paris Climate Agreement
-
More and more manufacturers are switching to renewable energy sources (e.g. car manufacturers)
-
The EU made its own Emissions Trading System
In addition, changes are not only taking place at the global level, but also at the business or even individual level. It is worth mentioning minimalism or zero waste as a movement.
The solution undoubtedly lies in renewable energy sources, but we still need to wait for this as the transition is extremely slow and cumbersome due to the reasons mentioned earlier.
