
Can renewable energy replace fossil fuels in the future?
Discover the shift towards cleaner energy sources. Can renewable energy replace fossil fuels in the future?
The growing global population and economic progress in numerous countries rapidly increase the energy demand. To satisfy the high demand, countries must intensify their energy generation efforts.
Relying solely on non-renewable energy sources proves infeasible due to their environmental consequences. However, innovative green technologies offer promising solutions.
What is the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy sources?
Renewable energy (clean energy)
Renewable energy, also known as clean energy, comes from natural sources that replenish themselves within human timeframes. We can utilize these sustainable sources without concern for depletion. They serve various purposes such as electricity generation, heating, and cooling. Clean energy sources typically have lower ecological footprints than fossil fuels.
Renewable energy sources include:
-
wind energy,
-
geothermal energy and
-
hydropower.
The United Nations defines renewable energy as follows:
"Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed. Sunlight and wind, for example, are such sources that are constantly being replenished. Renewable energy sources are plentiful and all around us."
Non-renewable energy
Non-renewable energy sources are inherently limited in availability. They will inevitably deplete, which poses a significant challenge for countries. These sources, unable to match the pace of consumption with their energy output, prove less suitable than green power sources.
Non-renewable energy sources include:
-
coal,
-
gas and
-
oil.
What is the current ratio of renewable to non-renewable energy use?
The below chart from Our World in Data illustrates a fourfold rise in global energy usage from 1965 to 2022, highlighting the increasing worldwide energy consumption.
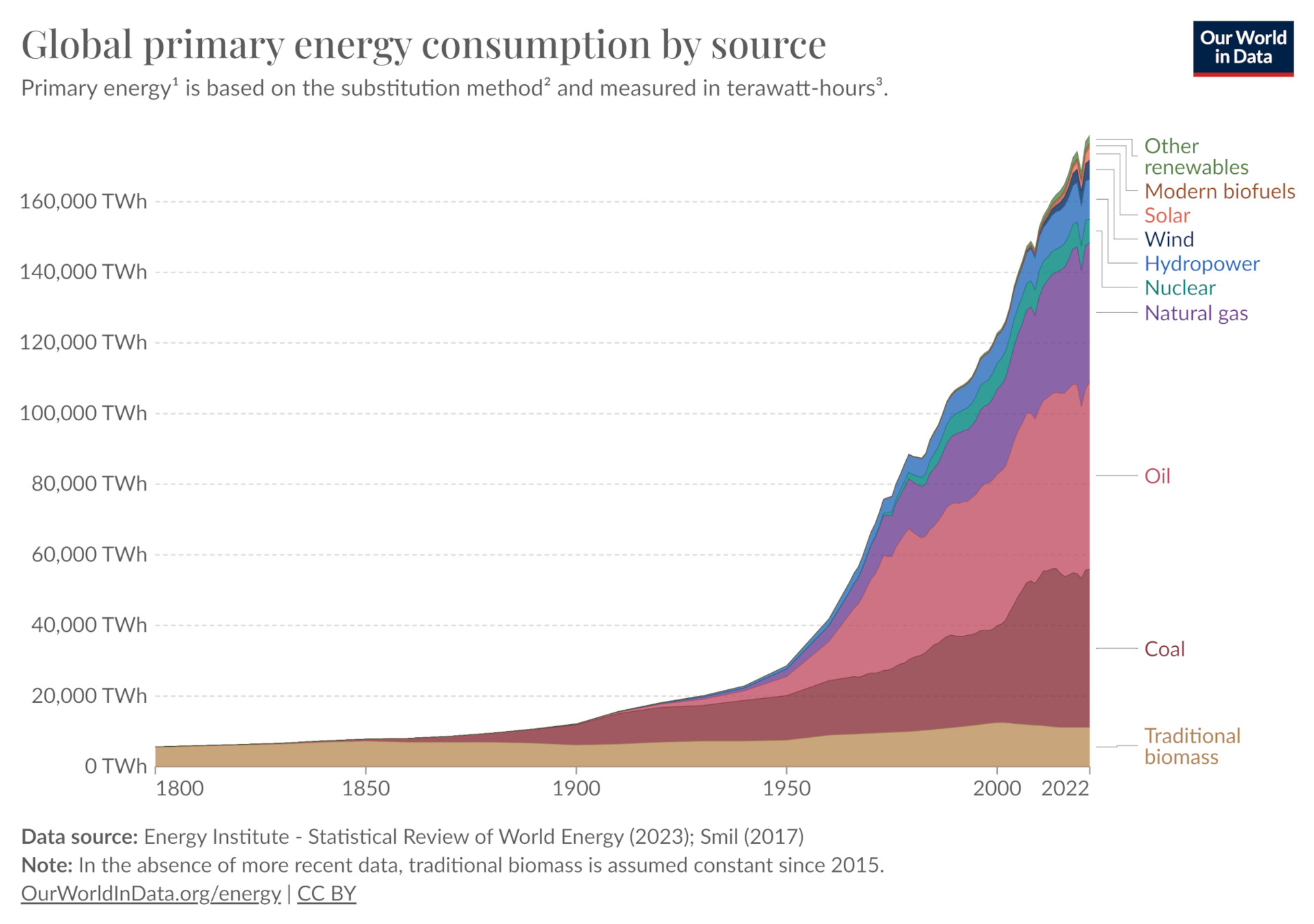
Source: ourworldindata.org
Currently, renewables contribute only 11.4% of the total global energy. Despite the continuous expansion in renewable energy source proportions, fossil fuels, including oil, coal, and gas, still dominate at an overwhelming majority. They account for 84.3% of all energy consumption.
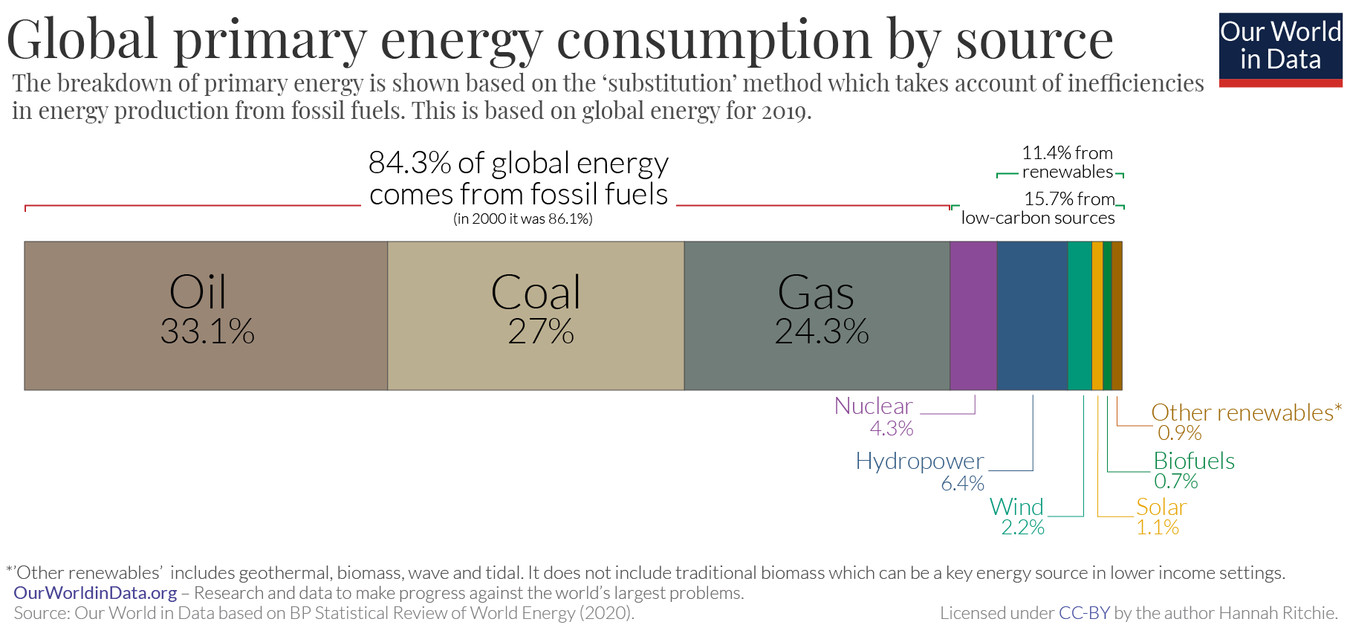
Source: ourworldindata.org
Low-carbon (nuclear) and renewable energy sources have surged from a mere 6% to nearly 18% over the past six decades, embodying an impressive trend. Despite this, one pivotal question persists: can renewable energy replace fossil fuels in the future?
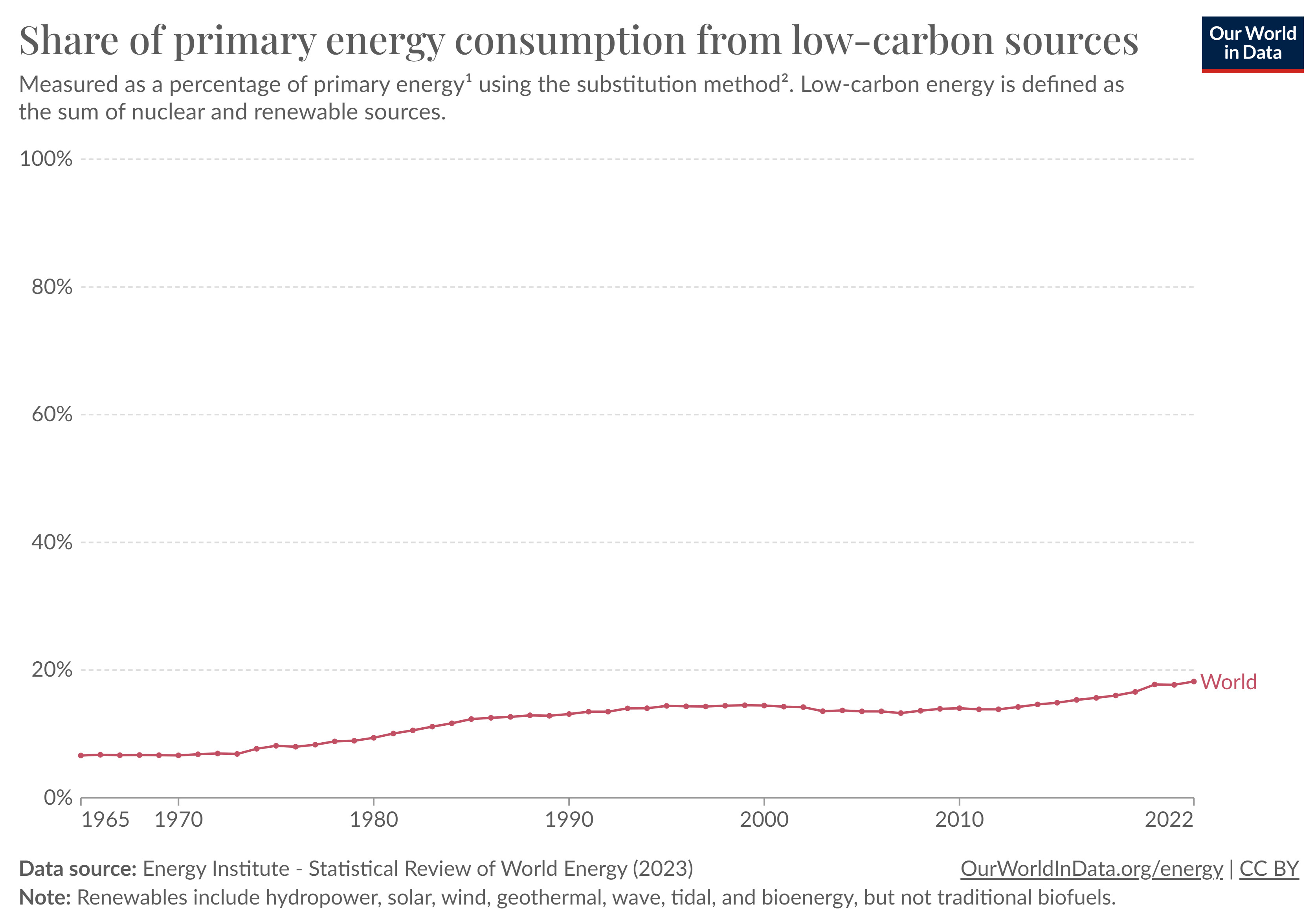
Source: ourworldindata.org
Can renewable energy replace fossil fuels in the future?
A complete transformation of our energy infrastructure is critical to achieve the replacement of fossil fuels. Currently, coal, gas, and oil supply over 80% of our energy.
A 2022 meta-analysis examined if renewable energy can replace fossil fuels by 2050. The study's conclusion can be summarized as follows:
-
By 2050, we must increase renewable energy production six-fold to eliminate fossil fuels under constant demand. Alternatively, an eight-fold increase is necessary with a projected population growth of 50%.
-
By 2050, a projected replacement of fossil fuels may be possible if the following conditions are met:
-
increase in energy demand by 25%,
-
a six-fold rise in renewables use,
-
doubling nuclear power capacity,
-
augmenting hydropower by 31%,
-
and limiting fossil fuel applications.
-
-
The transition presents challenges such as:
-
energy density,
-
a lack of consistency in supply due to weather conditions or other factors,
-
land availability
-
transportation issues.
-
-
Uncertain technological breakthroughs and robust international cooperation determine success.
Conclusion
Renewable energy can completely replace fossil fuels in the next 30 years, but it requires international cooperation and innovation. Natural gas could accelerate the shift towards a sustainable future. The cleanest hydrocarbon source could simplify the transition to green technologies.
Often, reliability limits the adoption of renewable options. For instance, solar panels generate minimal energy in the absence of sunlight. As an eco-friendly backup plan, natural gas can fasten the process of transition.
