
A complete guide to floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG)
Estimates predict a significant rise in global energy needs, with annual consumption projected to reach about 778 exajoules by 2035 as the world's demand steadily escalates. Innovations are crucial to fulfill the ever-growing demand: one such technology is floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG). It enables companies to tap into previously inaccessible offshore gas fields. Learn more about the FLNG technology in our comprehensive guide.
Why is natural gas (fossil gas) important?
Natural gas is a non-renewable hydrocarbon that is odorless, colorless, non-flammable, and non-toxic. Serving multiple purposes like electricity generation, transportation fueling, and heating, it presently fulfills 24.3% of global energy requirements.
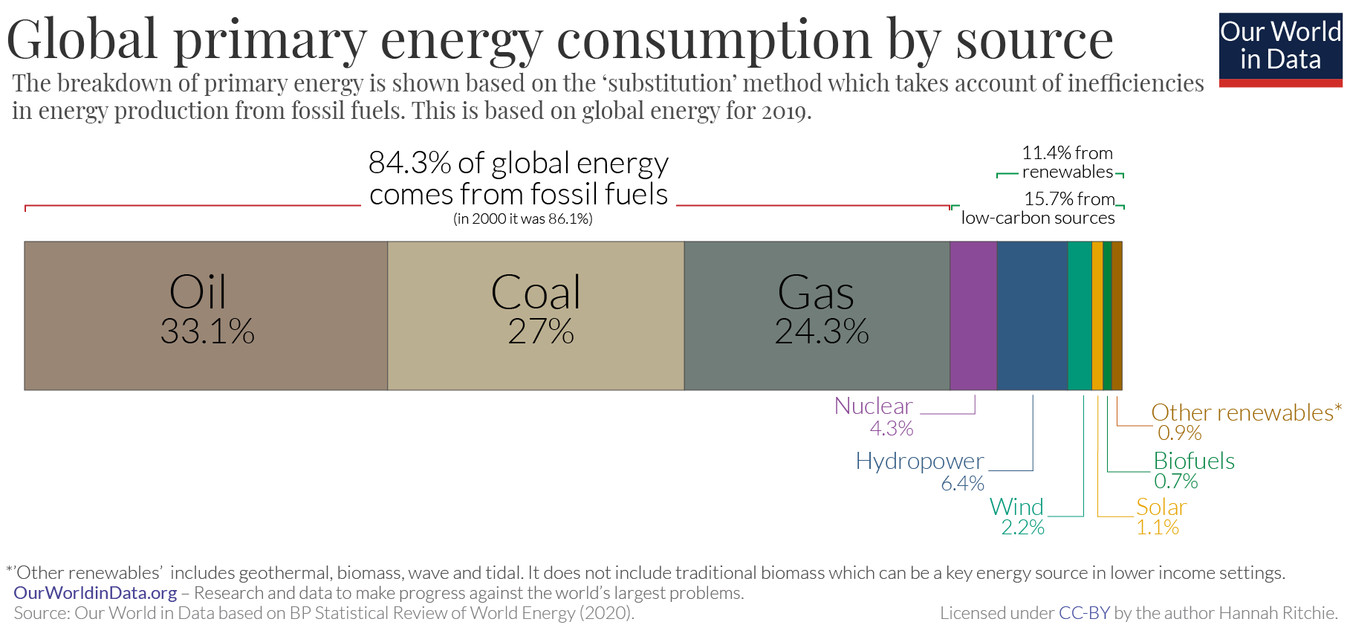
Source: ourworldindata.org
The primary advantages of natural gas include:
- In comparison to other fossil fuels, natural gas is highly cost-effective.
- Environmental friendliness, as it burns cleaner.
- It provides efficient storage and transportation.
- Natural gas can contribute to the faster adoption of green power technologies.
- Natural gas benefits are also evident in the security of the energy supply.
The global energy mix crucially relies on fossil gas. Yet, the extraction of natural gas from offshore fields at a distance poses challenges and may not be economically feasible. This is where FLNG technology comes into play.
What is floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG)?
Companies can now access underwater gas fields previously deemed economically or geographically challenging to reach, thanks to the innovative floating liquefied natural gas technology. Specifically designed FLNG vessels facilitate the production, liquefaction, and storage of natural gas at sea.
The process involves the following steps:
- Gas extraction: The pipeline delivers the gas to the processing plant on the ship.
- Purification: The treatment removes impurities such as dust, helium, water, acid gases, and hydrocarbons.
- Cooling: Vessels generating liquefied natural gas (LNG) shrink their volume to a size 1/600th smaller than that of regular natural gas. They cool the latter down to -162°C (-260°F).
- Storage: This transformation not only enhances safety during transportation but also improves cost-effectiveness significantly.
The benefits of floating liquefied natural gas
Floating liquefied natural gas technology offers a multitude of advantages – it not only lowers ecological impact but also provides significant economic benefits. This promising technology presents countless benefits for future energy production systems.
1. Economic opportunities
FLNG opens up previously inaccessible gas fields, offering many new economic opportunities. It can generate new business prospects for countries and boost their economic development.
2. Lower environmental footprint
All processing occurs on board, eliminating the need for extensive pipelines to the shore. Additionally, natural gas stands out as one of the cleanest and safest non-renewable energy sources.
3. Safety
Safety is a paramount feature of floating liquefied natural gas plants and vessels. Designed to withstand extreme storms, they ensure crew safety and prevent equipment damage.
4. Cost-efficient transportation
Given its volume which is 600 times smaller than natural gas, LNG offers considerably easier transportation. This directly translates to cost-effectiveness and simplicity in the logistics process.
5. Less vulnerability
Choosing FLNG over pipelines has strategic advantages as it is a safe and more stable transportation method. Unlike pipelines, which can be vulnerable to political tensions and attacks, FLNG reduces the risk of such incidents. This makes the transportation of natural gas more secure and reliable.

Conclusion
As the worldwide need for energy grows, there is a crucial demand for innovative technologies to meet these requirements. FLNG stands out as a key player in modern energy systems, because it has a smaller environmental impact than most other non-renewable sources. It is also cheaper to produce and easier to transport.
