
Natural gas has a pretty good reputation among fossil fuels. While burning this fossil fuel, it emits much fewer greenhouse gases than oil or coal. But we cannot say it is environmental-friendly: it is just less polluting.
How does natural gas affect the environment?
Natural gas environmental impact is based on 3 pillars:
- Drilling and extraction
- Transportation
- Burning and consumption
Drilling and extraction:
Drilling a well can affect wildlife and land use. With this intervention, local ecosystems could collapse: breaking migration patterns, pollute rivers and streams, causing erosion of dirt and pollutants are all side-effects of natural gas extraction. Hydraulic fracturing (fracking) can cause earthquakes and it overburdens the local water sources. This technique is part of the gas industry that an environmental protection agency would ban as soon as possible.
Read more: How is natural gas extracted?
Transportation:
Building an infrastructure to transport the gas from the wells to natural gas power plants is also a polluting process. Laying pipelines can cause habitat fragmentation and cross key areas from the perspective of nature. Gas leaks from pipes can cause big environmental trouble in the groundwater levels (and even on the surface).
Read more: Natural Gas Transportation.
Burning and consumption:
Natural gas is the most environmentally friendly fossil fuel because it burns cleaner. In power plants, natural gas emits 50 to 60 percent less carbon dioxide (CO2) than regular oil or coal-fired power plants. It also emits greenhouse gases with a lower life cycle into the atmosphere. However, combustion also releases methane and lowers air quality.
Natural gas environmental benefits
Statistics prove there are many benefits of natural gas. Among non-renewable energy sources, the emissions from its combustion are lower. Carbon dioxide emissions are the lowest with this material.
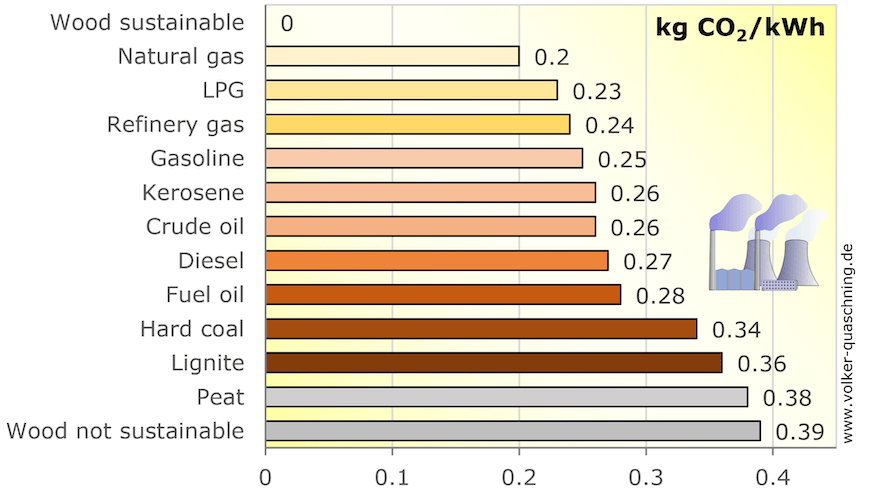
Source: https://www.volker-quaschning.de/datserv/CO2-spez/index_e.php
Natural gas is reliable: storing and transporting it is effective, thus the use of this energy is guaranteed. It is non-renewable, but the biggest problem with renewable energy is that we cannot store it effectively.
Price is not an environmental reason: natural gas is one of the cheapest sources of energy.
Is natural gas bad for the environment?
Every fossil fuel extraction is bad for the environment and increases our economic footprint. So if the question is “Is natural gas worse for the environment than solar power?”, the answer is yes. But if we ask “Is natural gas the most eco-friendly fossil power source?”, the answer is also yes.
The biggest threat of natural gas extraction is the process of fracking, using a lot of water from local water reservoirs and polluting the streams. Besides, this process releases methane into the air. While carbon dioxide emission is not that high, burning natural gas also releases methane, which is a strong greenhouse gas that leaks to the atmosphere in a big amount.
Burning natural gas also emits carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). It is also dangerous if not transported or extracted responsibly. Natural gas produce can end with an explosion if not shipped correctly. The problem with natural gas is its storing: the volume of the gas needs bigger storage places, which are costly to maintain.
A big disadvantage is that it is not renewable. According to Worldometers, only 52 years of natural gas reserves are left to extract. If you never want to run out of energy, you have to think about new sources besides natural gas.
Yet, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) tells that the global natural gas resource base is vast and more widely dispersed geographically than oil –so it is a more reliable source of energy.
Natural gas environmental impact: the future
According to new research, National Geographic tells us that natural gas is a much ‘dirtier’ energy source than we thought. This means methane emissions are an even higher impact than we thought.
Yet, a simple question remains unanswered: is natural gas (and methane) just a “bridge fuel” between fossil fuels and renewable energy, or will it remain with us for a long time?
While the signs from the environment suggest the first option, the market tells us just the opposite. Natural gas will not solve the global warming problem.
Conclusion: environmental effects of natural gas
The most environmental-friendly fossil fuel is natural gas. A gas-fired power plant’s emissions have 50 percent less carbon dioxide (CO2) during combustion compared to a coal power plant.
Key advantages:
- Cheap
- Has less carbon dioxide emissions than other fossil fuels
- Reliable
Disadvantages:
- Costly to store
- Dangerous: it could explode
- Has much more CO2 and methane emissions than solar or wind power
- Hydraulic fracturing can break natural habitats
Natural gas production does not solve the climate crisis, but it is the “lesser evil” option compared to other fossil fuels.
