
Not just the natural gas and its compounds have an impact on our environment, but the methods of extraction as well. Natural gas is a fossil fuel which means it cannot be produced without any environmental impact: but among other fossil fuels, it is still the cleanest and most efficient power source.
Environmental impact of natural gas
This illustration shows the production, transmission, and distribution of natural gas.
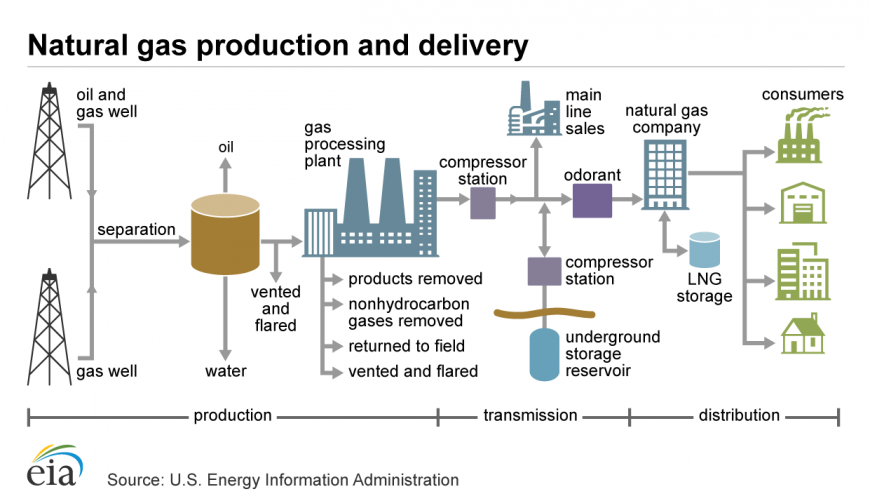
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration
Drilling and fracturing can happen on the sea with oil stands or land. Both have their risks to dump the nearby ecosystems. Because natural gas and oil often occur at the same place, first it is necessary to separate them. If natural gas cannot be transported, then gas will be vented and flared or reinjected into the ground to increase pressure in the oil reservoirs and make its production easier.
But if the infrastructure is developed, natural gas goes to the gas processing plant and to the compression station, to make it transportable.
Because natural gas is odourless, which can be dangerous, it also goes through the odorant process to get the ‘rotten egg’ smell. It is important and helps people to realize if there is a leaking point in the system.
From producers and natural gas companies, the gas gets shipped to factories, households, offices. Natural gas pipelines and resistant barrels are used to transport LNG (liquified natural gas).
The gas industry and power plants have an economic footprint for sure. Drilling and transporting can only happen with the breaking of wildlife habitats or deforestation.
How does natural gas affect the environment? – Extraction methods comparison
How is natural gas extracted? Shortly, there are 4 types of natural gas production:
- Vertical drilling
- Horizontal drilling
- Hydraulic fracturing/fracking
- Acidizing
While the first two have a small effect on the environment, hydraulic fracturing/fracking and acidizing have bigger impacts. Fracking is like a human-generated earthquake to free natural gas from impermeable rocks. This process needs huge quantities of water which can overwhelm the local eco-system and sometimes it empties water sources. Producers ‘inject’ water with sand and other chemicals into the ground with high pressure.
The result is toxic wastewater, which can leak into the ground and kill plants and animals. Acidizing has the same side-effect. It is a technique that dissolves rocks, so extracting will be easier.
Extraction does not necessarily end up with a catastrophe. This was the bad side of natural gas production, but still, the safest vertical drilling is the most popular. Bigger planning can prevent habitat breaking.
Natural gas pollution - greenhouse effects
Natural gas compounds:
- water,
- ethane,
- butane,
- propane,
- pentanes,
- hydrogen sulphide,
- carbon dioxide,
- water,
- helium,
- nitrogen
The gas used in our homes is almost completely methane. Drilling well releases methane into the air, which is a strong greenhouse gas. Flaming natural gas also releases CO, CO2, SO2, and NOx.
CO2 gas emissions are almost half compared to coal power plants.
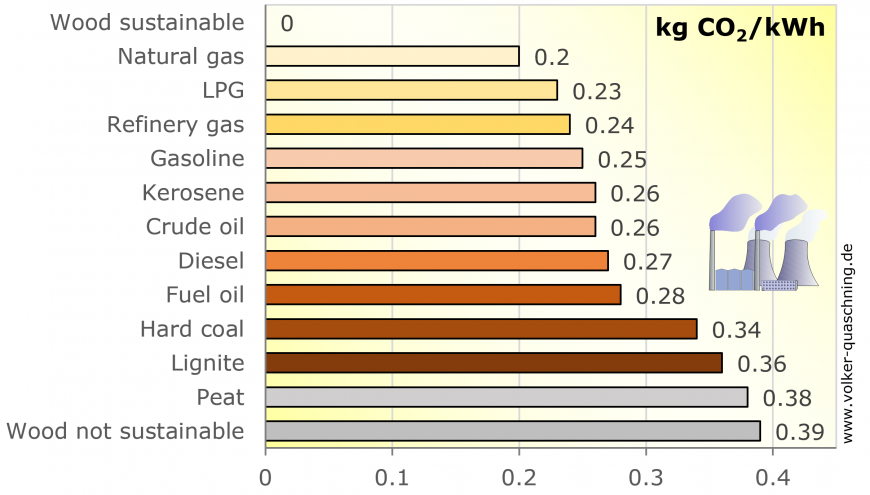
Source: Volker Quaschning
Methane emissions affect the atmosphere and the greenhouse effect 34 times stronger than CO2 over 100 years and 86 times stronger over 20 years. In a short time, it is more greenhouse gas than CO2.
Conclusion: is it an eco-friendly gas?
Natural gas is the most eco-friendly fossil fuel. It is also gaining popularity because its price is a big advantage. Natural gas is a bridge from hard coal and oil to renewable, clean energy.
Read more about the topic: Natural gas environmental impact
