
The energy sector is constantly changing, energy suppliers need to develop newer and newer technologies to generate, store, and transport energy to households and businesses. The energy industry is the basis of our civilization and economy. Without power plants, we would not be able to supply the planet’s whole population with electricity, gas, water, and food.
The parts of the energy sector
There are two parts of the energy industry: the one which provides renewable, green energy. And the other one that is more efficient but harms the environment: fossil fuels. Read more about the types of energy sources.
Renewable energy sources
Green power is infinite and less polluting than fossil fuels – yet, it still has some disadvantages.
- Hydropower
- Solar power
- Wind power
- Geothermal energy
- Biomass
While they are less polluting, maintaining large-area renewable energy plants can still harm the environment, changing the natural habitats of the locations. For example, wind power farms are harmful to birds.
Other than that, clean energy is renewable – but it is not available 24/7. The wind may blow on one day, but may not on the other. The sun may be shining today, but may not tomorrow. This could be a problem, especially for countries with long-night months in winter, because storing renewable energy is not easy.
Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels are:
- Oil and petroleum products
- Coal
- Natural gas
According to Worldometers, we will run out of oil in 47 years, natural gas in 52 years, and coal in 133 years. From the above-mentioned non-renewable fuels, natural gas is the most eco-friendly. Its price is lower and it has fewer greenhouse gas emissions than the others.
Read more about the current carbon emissions.
Changes in the energy market
The costs of energy sources differ and still, fossil fuels have the best price:
- gas/oil combined cycle power plant - $1000/kW
- geothermal - $2800/kW (2019)
- coal (with SO2 and NOx controls)- $3500–3800/kW
- advanced nuclear - $6000/kW (2019)
- onshore wind - $1600/kW (2019)
And because of that, petroleum products are consumed the most.
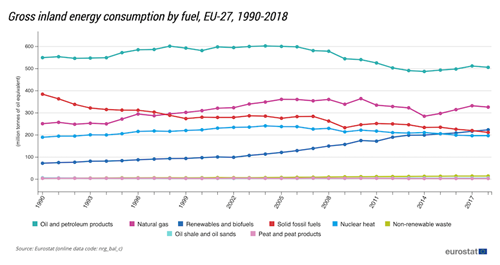
Source: Eurostat
Future of the energy industry
In the future, we will most likely use renewable energy sources. The biggest change compared to today’s energy usage is that nowadays we cannot store energy efficiently. Of course, you could sell the energy you produce, and maybe that is the future. Instead of one big energy supplier, small communities will be formed to share energy.
About the energy sector’s prices: as we are running out of fossil fuels, the price of oil and petroleum products will rise, while the development of non-renewable energy technology will lead to better prices in establishing wind or solar power plants.
Conclusion
- The energy industry is a basis for our civilization.
- Yet, fossil fuels have a more favourable price than green energy.
- To stop climate change, the energy sector must act now.
